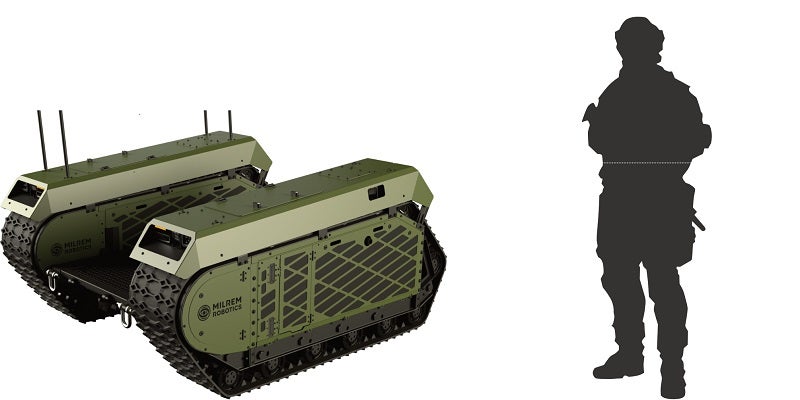
An integrated Modular Unmanned Ground System (iMUGS) consortium led by European developer Milrem Robotics has demonstrated the use of uncrewed systems by crewed units to conduct defence missions.
The event took place in Versailles, France, and was led by Safran and Nexter, with support from consortium members.
iMUGS members included project coordinator Milrem Robotics, Bittium, Diehl Defence, NEXTER Systems, Safran Electronics & Defense, Krauss-Maffei Wegmann, Latvijas Mobilais Telefons (LMT), Sol.One, Talgen Cybersecurity, dotOcean, GMV Aerospace and Defence, the Royal Military Academy of Belgium, and Insta Advance.
In the demonstration, the French armed forces used three Milrem Robotics’ THeMIS uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) that were fitted with payloads to perform autonomous mission planning, re-supply and casualty evacuation, intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR), and cyber threat responses.
iMUGS Consortium lead Milrem Robotics CEO Kuldar Väärsi said: “Uncrewed systems increase stand-off distance from the enemy and, thanks to various sensors and effectors, provide soldiers the means to gather a higher quantity and much more precise information about their operation area than humans are capable of.”
Väärsi added: “Autonomous unmanned assets are a game changer for armed forces as they allow the allocation of soldiers to more important tasks.”
The event is the fifth of six demonstrations that are to be carried out to display the iMUGS project’s progress.
Four demonstrations have already been conducted in Estonia, Latvia, Finland, and Belgium, with the final one to be performed in Germany in December.
The €32.6m iMUGS project is focused on developing the European standard uncrewed ground system and involves building a modular and scalable architecture for hybrid crewed and uncrewed systems.
During the demonstration, the UGVs were fitted with Saab Grintek’s laser warning system, Escribano Mechanical & Engineering’s electro optic system, Bittium’s software defined radios, and Metravib Defence’s PEARL acoustic shot detection.
Diehl Defence, Milrem Robotics, Nexter, and Safran developed the UGV’s autonomous follow-me, waypoint navigation and obstacle detection, and avoidance capabilities.
In addition, OTEOS provided ISR, Talgen offered cyber threat responses, and global and local swarming capabilities were delivered by dotOcean and Insta.
Krauss-Maffei Wegmann’s Boxer armoured personnel carrier (APC) featured the command and control (C2) and tactical C2ISR offered by GMV and sol.one. The APC also had a C2 mission module and a static command centre.